GridFS with GoLang (Part 1)
Lately, I have been working on building a server that stores and manages files sent by respective client. This was the first time when I had to build a full fledged HTTP server with a compatible database to store files of any size (GBs too).
After reading multiple related blogs, I was able to deduce the following plan for my server:
- Build HTTP server & respective routes using net/http package.
- The server will initiate a connection with MongoDB to perform CRUD operations.
- But, to bypass the
16 MBfileSize limit of MongoDB, I had to take the GridFS feature into consideration.
Though GridFS eases the management of files, but, GridFS with Go was a learning curve for me.
While I am writing this, there are really few documentations that could help with all the CRUD operations. Apparently, I did manage to meet the requirements using GridFS with go, and hence, here I am to share my journey.. 😉
➤ What is GridFS ??
GridFS basically is a specification that allows to manage the files with size above 16 MB. As we all must be aware that MongoDB stores data records as “BSON documents” inside a collection.
So, instead of storing the complete file as a single document, which might lead to a document of size above 16MB, GridFS
- divides the files into parts (termed as
chunks), - and stores each chunk as a seperate document.
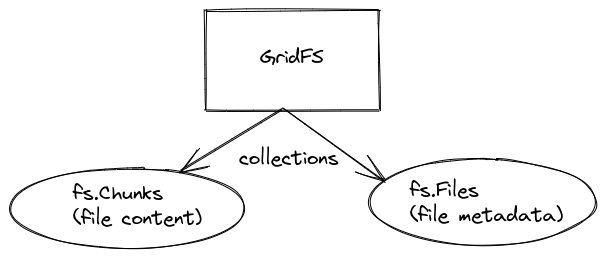
In addition to this file’s content management, GridFS also takes care of managing the metadata of each file. This is done via two different collections; i.e., fs.Chunks and fs.Files
Now that we have discussed the basic components I’ll be using to build my server, let’s move to the next part to dive into the implementations.
